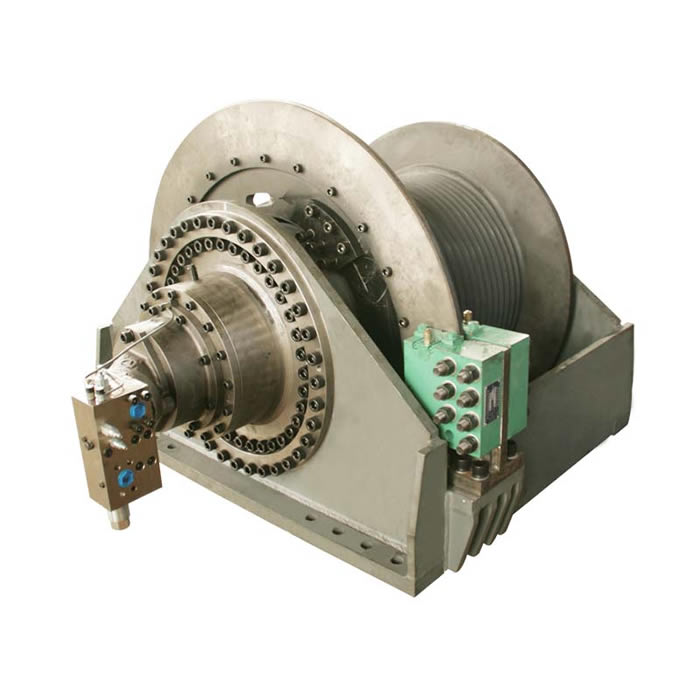
Some requirements for control valves in hydraulic cylinders

When selecting a Hydraulic Cylinder, whether the control valve is reasonable or not will have a great impact. When selecting a control valve, we mainly consider two aspects, one is the selection of the proportional directional valve, and the other is the selection of the pressure compensator.
Generally, different valve components can be combined together according to the needs. For example, the proportional directional valve for throttling control of the hydraulic cylinder can be used together with the constant pressure reducing valve to form a proportional directional flow valve for differential pressure compensation. The control flow of this flow valve mainly depends on the input signal and is not affected by pressure and load pressure changes.
After the pressure difference is determined, the flow rate of the proportional directional valve of the equipment can be determined as follows: the input signal corresponding to the larger flow rate actually passing through the proportional directional valve should be close to 90% of the rated input signal, and the input signal corresponding to the smaller flow rate actually passing through the proportional directional valve It should be larger than the area of the proportional directional valve, which can not only increase the flow resolution, but also avoid the problem of crawling.
Then, when selecting a pressure compensator, the pressure compensator of the hydraulic cylinder generally adopts a two-way and three-way structure.
This effect disappears if the actuator is negatively loaded. In order to avoid this problem, we can use a balance valve with back pressure, so that the pressure difference at the proportional valve port does not change with the fluctuation of the load.